ES6相关
var、let、const 的区别
1 作用域 let、const 存在块级作用域 var 不存在块级作用域
2 const 常量 定义时赋值
3 变量提升 let/const 声明的变量需要声明后使用 var 声明的变量可以声明前使用
4 重复声明 let/const 不能重复声明 var 可以重复声明
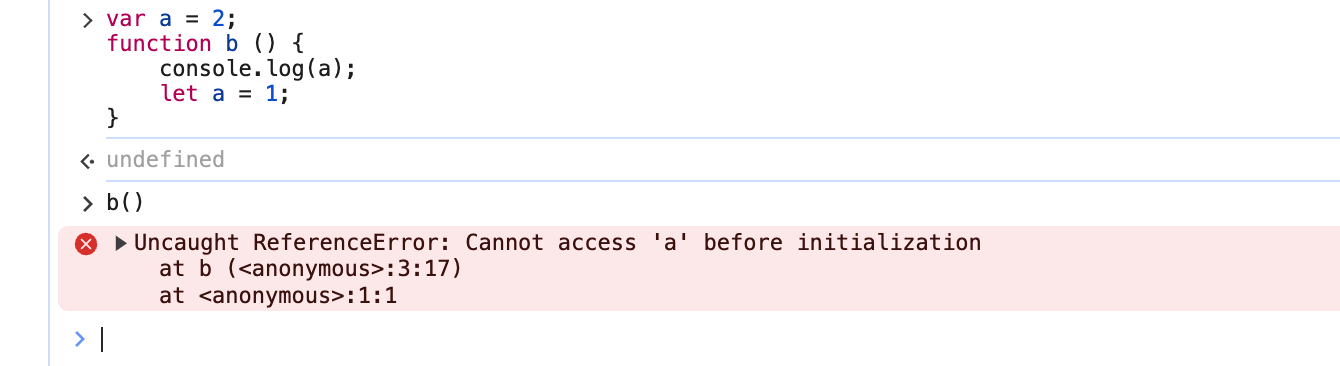
5 暂时性死区 let/const 声明的变量不能在声明前使用
箭头函数和普通函数的区别
1 箭头函数没有 arguments
2 箭头函数没有自己的 this this 由定义的所在父级上下文决定
3 箭头函数继承来的 this 不会改变 call、apply、bind 方法不能改变箭头函数的 this 指向
js
var id = 'global';
var obj = {
id: 'obj',
a: function () {
console.log(this.id);
},
b: () => {
console.log(this.id);
}
}
obj.a(); // obj
obj.b(); // global
const a = obj.a;
a(); // global
const b = obj.b;
b(); // global
new obj.a(); // undefined
new obj.b(); // Uncaught TypeError: obj.b is not a constructorvar id = 'global';
var obj = {
id: 'obj',
a: function () {
console.log(this.id);
},
b: () => {
console.log(this.id);
}
}
obj.a(); // obj
obj.b(); // global
const a = obj.a;
a(); // global
const b = obj.b;
b(); // global
new obj.a(); // undefined
new obj.b(); // Uncaught TypeError: obj.b is not a constructorjs
var id = 'global';
const fun1 = () => {
console.log(this.id);
}
fun1(); // global
fun1.call({ id: 'call' }); // global
fun1.apply({ id: 'call' }); // global
fun1.bind({ id: 'call' })(); // globalvar id = 'global';
const fun1 = () => {
console.log(this.id);
}
fun1(); // global
fun1.call({ id: 'call' }); // global
fun1.apply({ id: 'call' }); // global
fun1.bind({ id: 'call' })(); // global4 箭头函数不能作为构造函数 因为没有 prototype 属性
5 箭头函数不能作为 Generator 函数,不能使用 yield 关键字
Proxy
用来代理对象
js
// target 要代理的对象
// handler 代理对象的行为
let p = new Proxy(target, handler);
let onWatch = (obj) => {
let handler = {
// target 目标对象,property 目标对象的属性,receiver Proxy 实例本身
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log(`getting ${property}!`);
return Reflect.get(target, property, receiver);
},
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log(`setting ${property}!`);
return Reflect.set(target, property, value, receiver);
}
}
return new Proxy(obj, handler);
}
let obj = { a: 1 };
let test = onWatch(obj);
test.a // getting a!
test.a = 2 // setting a!// target 要代理的对象
// handler 代理对象的行为
let p = new Proxy(target, handler);
let onWatch = (obj) => {
let handler = {
// target 目标对象,property 目标对象的属性,receiver Proxy 实例本身
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log(`getting ${property}!`);
return Reflect.get(target, property, receiver);
},
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log(`setting ${property}!`);
return Reflect.set(target, property, value, receiver);
}
}
return new Proxy(obj, handler);
}
let obj = { a: 1 };
let test = onWatch(obj);
test.a // getting a!
test.a = 2 // setting a!