Canvas 尺寸与分辨率矫正
前言
Canvas 的默认大小为 300 像素 ×150 像素(宽 × 高,像素的单位是 px)
<canvas id="tutorial" width="150" height="150"></canvas><canvas id="tutorial" width="150" height="150"></canvas>canvas 看起来和 img 元素很相像,唯一的不同就是它并没有 src 和 alt 属性。实际上,canvas 标签只有两个属性: width 和 height。
正文
设置画布的 css 大小
canvas 可以使用CSS来定义大小,但在绘制时图像会伸缩以适应它的框架尺寸:如果 CSS 的尺寸与初始画布的比例不一致,它会出现扭曲。
假设一个场景,当我们给 canvas 设置了 css 的宽高 500px * 500px, 但是我们在 canvas 中绘制的图形是 100px * 100px, 那么最终的图形会被拉伸,如下图所示:
<canvas id="test-canvas"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('test-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.fillStyle = 'red';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "500px";
</script><canvas id="test-canvas"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('test-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.fillStyle = 'red';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "500px";
</script>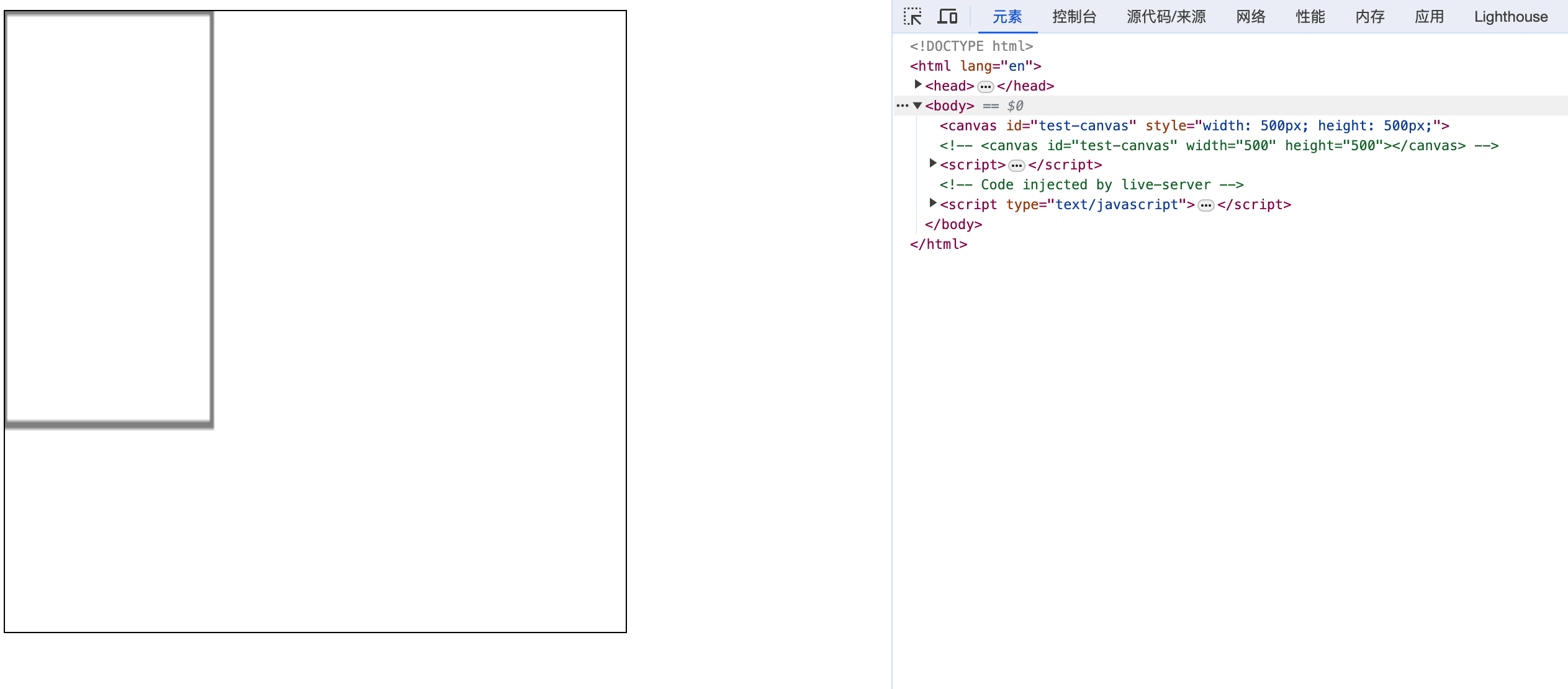
因此,如果你想绘制一个 100px × 100px 的正方形,而且你的 CSS 代码中设置了 width: 500px; height: 500px;,那么最终图像将会是一个扁平的正方形。
设置画布的属性大小
从上面的案例我们发现,当我们设置了 canvas 的 css 大小后,canvas 会被拉伸,那么我们可以通过设置 canvas 的属性 width、height 来解决这个问题。
<canvas id="test-canvas" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('test-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.fillStyle = 'red';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "500px";
</script><canvas id="test-canvas" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('test-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.fillStyle = 'red';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "500px";
</script>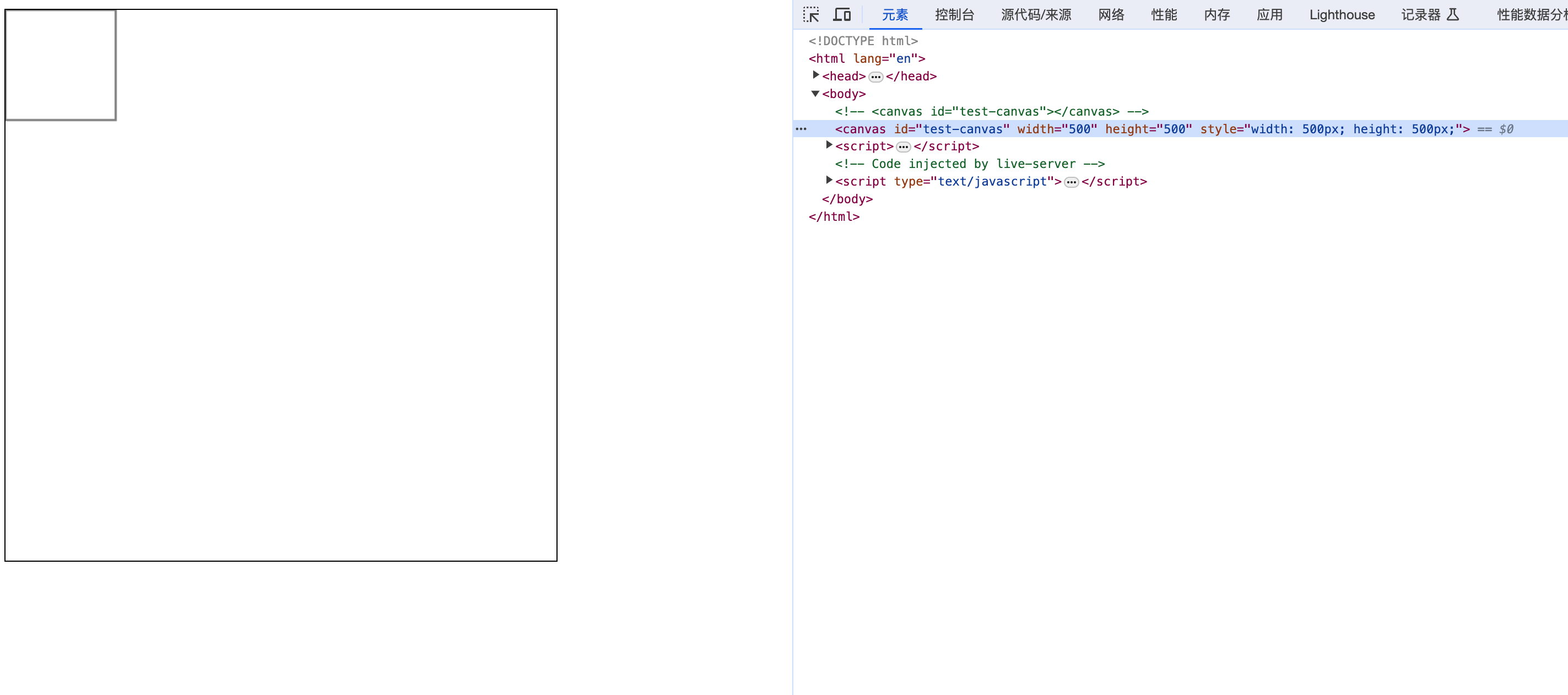
当我们设置了 canvas 的属性 width、height 后,canvas 的大小就固定了,不会被拉伸,但是我们在 canvas 中绘制的图形是 100px * 100px, 那么最终的图形也显示正常了
备注: 如果你绘制出来的图像是扭曲的,尝试用 width 和 height 属性为<canvas>明确规定宽高,而不是使用 CSS。
Canvas分辨率矫正
通过上面的案例,虽然我们的正方形没有变形,但是边框很模糊(图片截图可能看的不是很明显)。这是因为不同DPR下,绘制100px的图形所需要的像素不同。比如同样是100px的元素,如果在DPR为1的屏幕上,只需要100的像素,此时就很清晰。但是如果在DPR为2的屏幕上,就需要200像素,但实际上canvas绘制时,只绘制了100px。具体可以看这里。下面的代码就是用于矫正canvas的分辨率:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Canvas 实验</title>
<style type="text/css">
canvas {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="test-canvas" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
const dpr = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
console.log(`dpr--->`, dpr);
const canvas = document.getElementById('test-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "500px";
canvas.width = 500 * dpr;
canvas.height = 500 * dpr;
ctx.scale(dpr, dpr);
ctx.strokeRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Canvas 实验</title>
<style type="text/css">
canvas {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="test-canvas" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
const dpr = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
console.log(`dpr--->`, dpr);
const canvas = document.getElementById('test-canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
canvas.style.width = "500px";
canvas.style.height = "500px";
canvas.width = 500 * dpr;
canvas.height = 500 * dpr;
ctx.scale(dpr, dpr);
ctx.strokeRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
</script>
</body>
</html>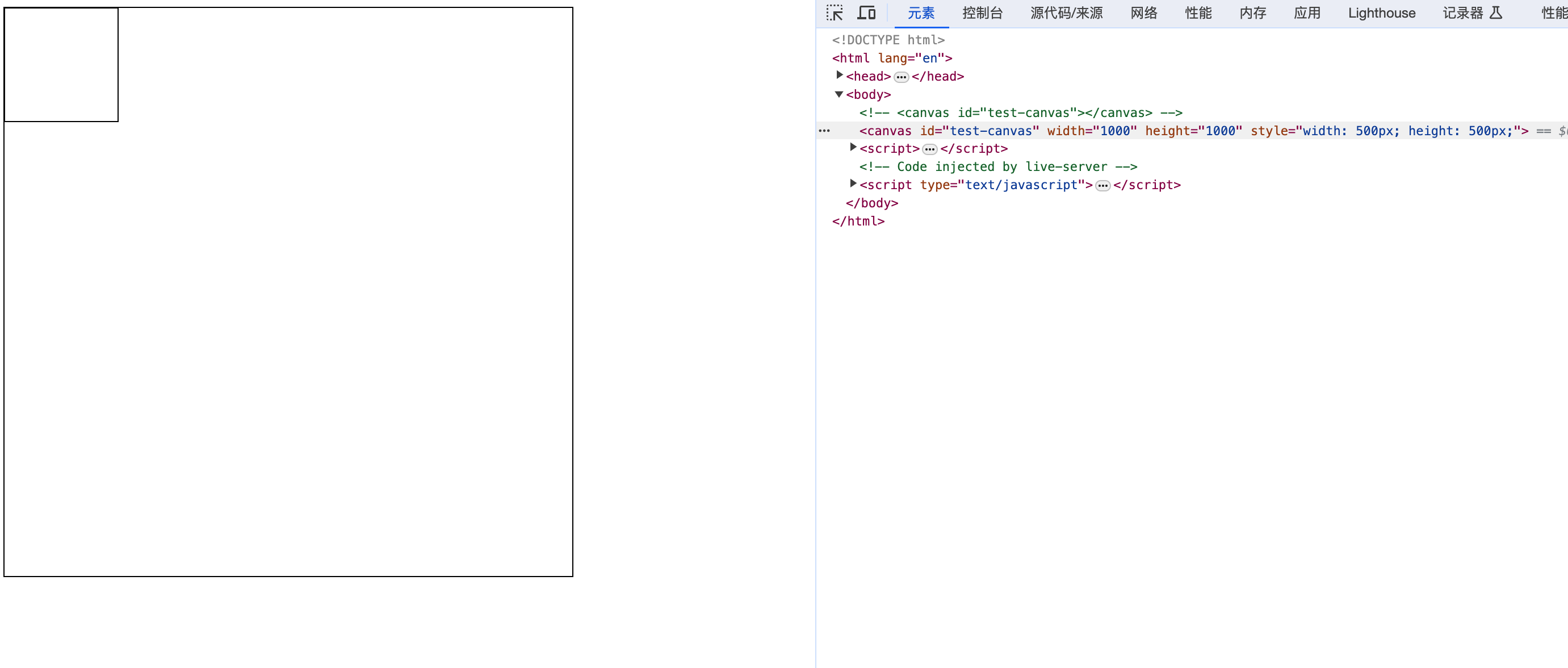
当我们将 canvas 的尺寸乘上像素比后,再将 canvas 的尺寸缩小到原来的 css 尺寸,这样就可以保证 canvas 1px 绘制所需要的像素一致,从而保证绘制出来的图形不会模糊。
监听 dpr 变化
当用户进行页面切换或者将浏览器放置到其他屏幕时,dpr 可能会发生变化,因此我们需要监听 dpr 的变化,从而重新绘制 canvas。
由于在下使用的技术栈是 React。因此通过监听 window 的 change 事件,从而重新调整 canvas 的尺寸。
export function useDevicePixelRatio() {
const [dpr, setDpr] = useState(window.devicePixelRatio || 1);
useEffect(() => {
const update = () => {
setDpr(window.devicePixelRatio || 1);
};
window.addEventListener('change', update);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('change', update);
};
}, [dpr]);
}
<canvas
width={width * dpr}
height={height * dpr}
style={{
width: `${width}px`,
height: `${height}px`,
}}
></canvas>
// 这时候我们还需要重新缩放 ctx
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.setTransform(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0); // scale 前先恢复变换矩阵,不然会重复 scale
ctx.scale(dpr, dpr);export function useDevicePixelRatio() {
const [dpr, setDpr] = useState(window.devicePixelRatio || 1);
useEffect(() => {
const update = () => {
setDpr(window.devicePixelRatio || 1);
};
window.addEventListener('change', update);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('change', update);
};
}, [dpr]);
}
<canvas
width={width * dpr}
height={height * dpr}
style={{
width: `${width}px`,
height: `${height}px`,
}}
></canvas>
// 这时候我们还需要重新缩放 ctx
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.setTransform(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0); // scale 前先恢复变换矩阵,不然会重复 scale
ctx.scale(dpr, dpr);